Steel E-Motive Steel Materials and Technologies Portfolio: A Recipe for Innovation
A blog by George Coates – Technical Director, Steel E-Motive and WorldAutoSteel
Twenty-five years ago the UltraLight Steel Auto Body Consortium launched a global effort to demonstrate what was then the most advanced steels ever produced, High-Strength Steels (HSS). At the time, with just 11 HSS grades available, ULSAB reduced mass by 25% over benchmarks and featured cutting edge technology such as a tailor-welded body side outer that reduced part count from 3 or 4 pieces to one efficient structure (Figure 1). Tailor welding enables the joining of different material grades and thicknesses into one blank for stamping a part, thereby placing higher strength levels exactly and only where they are needed. A one-piece body side outer and tailor welding is commonplace today because of the efficiency it lends to vehicle design and manufacturing.
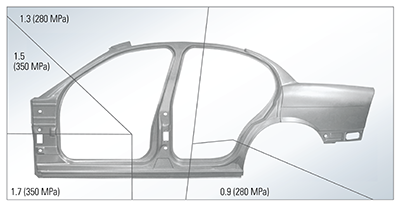
Figure 1
ULSAB’s cutting edge one-piece body side outer employed one of the first uses of its kind for tailor-welding technology in vehicle design and manufacturing.
The four programs that followed ULSAB produced steel innovations that influenced vehicle design and manufacture for the past decades. Steel E-Motive follows this long history of demonstrations of steel technologies that are expected to be commercially available in 2030 and beyond. With the portfolio of steel product and manufacturing processes already available and the addition of those forecasted for future commercial availability, we are expecting innovations that will be a roadmap for future mobility vehicle manufacturers.
What is the significance of AHSS Strength vs Elongation?
Higher strength levels mean steel parts can be manufactured at minimum thickness while still meeting the strength requirements for crash and performance. The results are lighter and more environmentally efficient components because less material is used. But increasing strength and thinner gauges makes forming complex component shapes a challenge. 3rdGen AHSS have increased elongation as well as increased strength. Elongation is a material mechanical property that is the degree to which a material may be bent, stretched, or compressed before it breaks. With high elongation, complex vehicle component shapes can be formed and manufactured more easily, resulting in strong, efficient structures.
Global steelmakers are investing significantly in product and fabrication development. High Strength and Advanced High-Strength Steels (AHSS) portfolios have grown from ULSAB’s 11 to more than 50 grades available for use in designing and optimizing Steel E-Motive’s autonomous EV architecture. Third Generation AHSS (3rdGen AHSS), which will have a prominent role in Steel E-Motive’s architectures, are taking strength levels ever higher while addressing manufacturability. Our members are producing 3rdGen AHSS that can be cold-formed with strength levels upwards of 1200 MPa, due to elongations of 20% and greater, which completely opens the manufacturing window of possibilities.
Steel and Manufacturing Technologies
To further assist in the design and manufacture of efficient vehicle structures, new processes such as roll forming and hot forming help fabricate these stronger materials effectively, while often doubling material use efficiency. This means less material is produced for each component, resulting in a significant reduction in manufacturing emissions and, ultimately, an improved vehicle environmental footprint.
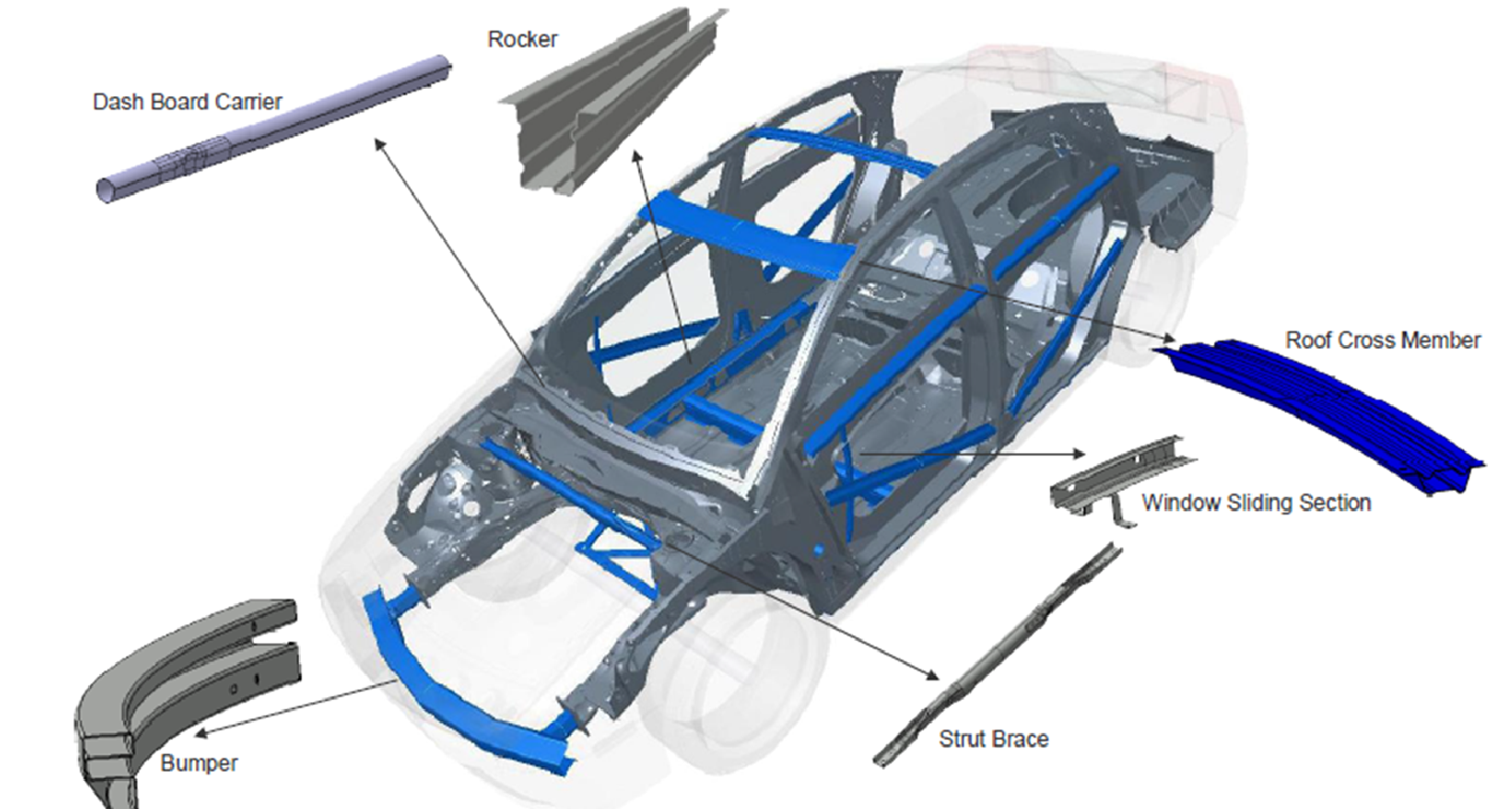
Figure 2
Vehicle body structure parts suitable for the roll forming process.
Roll Forming takes a flat sheet or strip and feeds it through a mill containing several successive roller dies, each of which incrementally bend the strip into the desired final shape. Incremental forming minimizes certain stresses and strains on the material that inhibit part formation with very high strength materials. Therefore, roll forming is well suited for generating many complex shapes from Advanced High-Strength Steels, even and especially for those grades with low total elongation. Unlike most forming operations which have various combinations of forming modes, the roll forming process is nothing more than a carefully engineered series of bends. Roll forming is appropriate for high-volume applications requiring long, complex sections held to very precise dimensions, such as a bumper, rocker or truck bed (See Figure 2 for more examples).
These are just two of many processes that will be a part of the materials and processes portfolio for manufacturing Steel E-Motive vehicle components. (See Figure 3 for more examples.)
Steel E-Motive Example steel and steel technologies portfolio
Steel Grades
- Complex Phase
- Dual Phase, High Formability
- Quench & Partition
- Ferrite-Bainite
- Manganese-Boron
Steel Technologies
- Laser Welded Blanks
- Tailor Welded Blanks
- Tailor Rolled Blanks (quenched steel)
- Laser Welded Coil
- Laser Welded Hydroformed Tubes
- Sheet Hydroforming
- Tube Hydroforming
- Roll Forming
- Roll Stamping
- Press Hardening
- Laser Welded Tube Profiled Sections
- Multi-Walled Hydroformed Tubes
- Multi-Walled Tubes
As engineering progresses, we’ll be revealing the Steel E-Motive innovations that will result from the unique and efficient designs that advanced steels and steel technologies enable. Be sure to subscribe to receive updates.


George Coates
Subscribe for updates
The Steel E-Motive vehicle concept is still in development. Sign up to be the first to hear about the latest developments from the program.
